Maximization of network efficiency
through the automatic distribution of traffic
Load balancer
This feature automatically distributes inbound traffic to prevent traffic bottlenecks and to ensure efficient network operation.
-
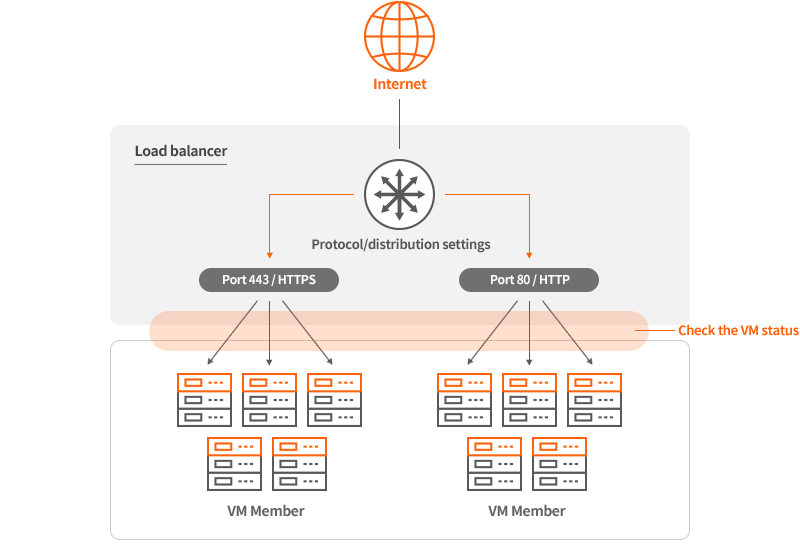
Single Zone LB
- This is a load balancer for distributing traffic within a single zone.
- You can register two or more instances belonging to the zone in question as load balancing members. -
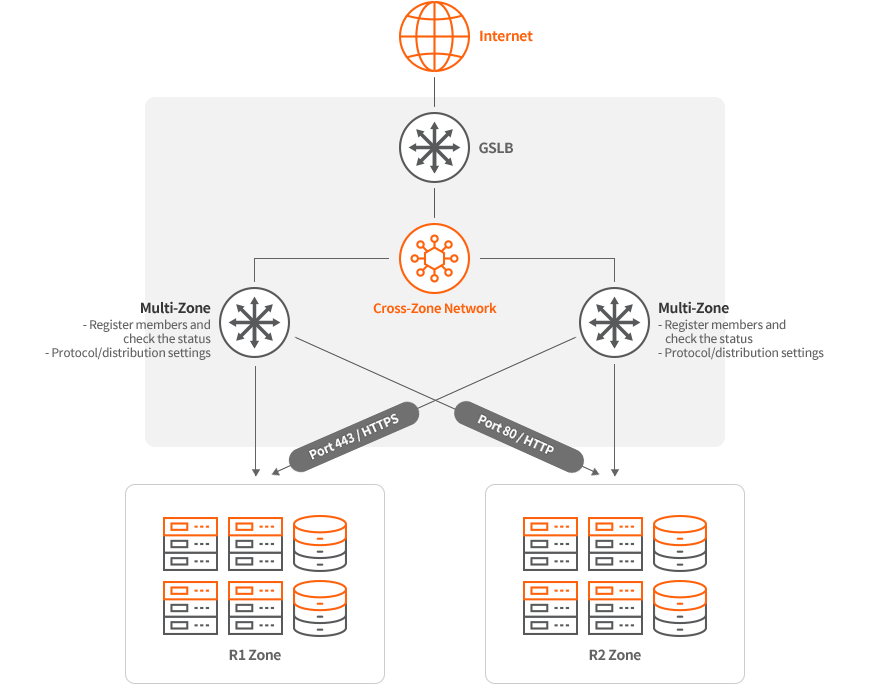
Multi-Zone LB
- This is a load balancer for distributing traffic between two or more zones within a multi-zone.
- It provides DNS-based GSLB service, and a load balancer is created and operated in each zone.
- Load balancing members can be registered in other zones using the cross-zone network.
Contact an Expert
Price

Load Balancer 2.0 can create a single zone LB and multi-zone LB.
| Product | Specification | Hourly Rate | Max. Number of Concurrent Connections | TPS | Common |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Zone LB | 2Core 2GB From 2 (default) to 4 |
KRW 30 | 80,000~160,000 | 60,000~120,000 | - |
| Multi-Zone LB | 2Core 2GB (in 2 zones) From 2 (default) to 4 |
KRW 70 | 80,000~160,000 | 60,000~120,000 | GSLB provided Redundant configuration between zones |
- TPS(transactions per second): Number of transactions that the system can handle per second
* For products with higher specifications, request a standalone load balancer service.
How to Use

1. Create a pool with the protocol and distribution method of the load balancer settings configured.
2. Create a VIP (virtual IP address) connected to a public IP address.
3. Register VMs to distribute the load according to the pool settings with the LB members.
4. Set the monitoring value for load balancer management.
5. Connect the VIP to the public IP address where the load balancer will be used, and the traffic coming into the public IP address in question will be distributed.
Features
- Distribution of traffic coming into a specific IP address
- Ensuring stability by configuring redundancy (Active-Standby) with the application of failover
- Can select the protocol and distribution method according to your needs
-
Types of Supported Protocols :
- TCP, HTTP, HTTPS -
Distribution Methods :
- Round robin, a way of directing the same amount of requests to the designated servers sequentially
- Source IP, a way of directing a specific IP request to a specific server
- Least connection, a way of direct the request to the server receiving the least requests
-
Types of Supported Protocols :
Configuration

- Single-Zone LB
- Multi-Zone LB